Navigating Dementia: Common Questions Answered
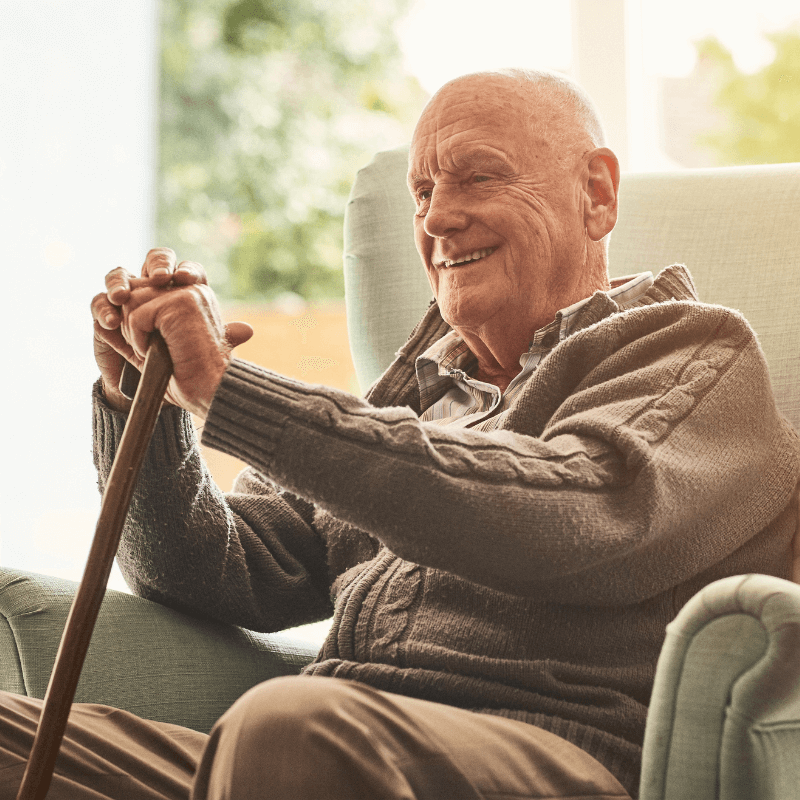
Dementia is a complex condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Here, we explore some common questions about dementia. Whether you’re seeking to understand the early signs, causes, diagnosis, or ways to support a loved one, this information will help you navigate this journey.
Are Dementia and Alzheimer’s the Same?
While often used interchangeably, dementia and Alzheimer’s are not the same. Dementia is an umbrella term for a range of conditions that cause a decline in cognitive function—severe enough to interfere with daily life. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia. Alzheimer’s accounts for 60-80% of cases. Other types of dementia include vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, and frontotemporal dementia.
What Are the Early Signs of Dementia?
Early signs of dementia can vary, but common symptoms include:
- Frequent memory loss, especially of recent events.
- Becoming repetitive, asking the same question over and over.
- Trouble finding the way to familiar places.
- Trouble concentrating and getting confused mid-task.
- Problems understanding written or spoken words.
- Difficulty in planning or solving problems.
- Trouble with spatial awareness and judging distances.
- Misplacing things and losing the ability to retrace steps.
- Withdrawal from work, social activities, family, and friends.
- Changes in mood and personality, such as becoming confused, suspicious, or depressed.
- Neglecting housework or personal hygiene.
How Dementia is Caused
Dementia can affect anyone, though it’s more common in people over the age of 65. Cognitive decline is usually a result of damage to brain cells caused by a range of conditions.
The likelihood of developing dementia depends on its specific cause. Approximately one-third of those with Alzheimer’s disease have a close relative, such as a parent or sibling, who also has dementia. However, many cases arise without any family history of the condition. Primary causes of dementia include:
- Alzheimer’s disease.
- Vascular issues such as strokes.
- Lewy body disease and Parkinson’s disease.
- Frontotemporal degeneration.
- Chronic alcohol abuse.
- Certain types of infections.
- Traumatic brain injury.
Risk factors such as age, genetics, and lifestyle choices like smoking, poor diet, and lack of exercise can also increase the likelihood of developing dementia.
How Dementia is Diagnosed
Diagnosing dementia involves a thorough evaluation. This will identify the type and extent of cognitive damage and rule out other possible causes. An assessment may typically involve:
- A medical history review.
- Physical and neurological examinations.
- Cognitive and neuropsychological tests.
- Brain imaging such as an MRI, CT scan, PET, and SPECT.
- Cerebrospinal fluid protein tests.
Can Dementia Be Cured?
Currently, there is no cure for dementia. However, some treatments can help manage symptoms. Medications, therapies, and lifestyle changes can improve quality of life and slow the progression of certain types of dementia. Research is ongoing, and new treatments are continually being explored.
What Are the Stages of Dementia?
Dementia progresses through several stages. Each stage has distinct characteristics.
- Mild (Early Stage): This stage involves minor memory lapses, difficulty handling complex tasks, and slight personality changes. Individuals may forget recent events or familiar names and struggle in social settings.
- Moderate (Middle Stage): Memory loss and confusion become more significant. Individuals may require help with daily activities, experience behavioural changes, and have trouble with trouble communicating and understanding.
- Severe (Late Stage): In the severe stage, memory loss is profound, and individuals may not recognise loved ones. They lose the ability to perform basic tasks independently and often require full-time care due to significant physical and cognitive decline.
How Can I Support a Loved One with Dementia?
Supporting a loved one with dementia involves patience, understanding, and practical assistance. Here are some tips:
- Educate Yourself: Learn about dementia and its effects.
- Communicate Clearly: Use simple language and be patient.
- Create a Safe Environment: Remove hazards and create routines.
- Encourage Independence: Allow your loved one to do as much as possible on their own.
- Seek Support: Utilise home care services like Simply Helping to make daily life more manageable for both you and your loved one.
- Take Care of Yourself: Caregiving can be demanding, so ensure you also look after your own wellbeing.
*Extra tips to support someone living with dementia can be found by clicking here.
Where Can I Get Help?
If you have concerns about dementia, your first step should be to visit your GP for an initial assessment and guidance. For further assistance and information, a great resource is the Dementia Australia Helpline at 1800 100 500. They provide support, resources, and advice to help you manage dementia.
At Simply Helping, we offer a range of home care services to support individuals living with dementia and their families. Our experienced teams provide the following services:
- Personal care
- Home help
- Social support
- In-home respite care
- Gardening and lawn mowing
- Community nursing
- Pet sitting and dog walking
- Transport services
Click here to find a Simply Helping location near you and see how we can help.